The Dynamic Role of WANs in Modern Network Infrastructure
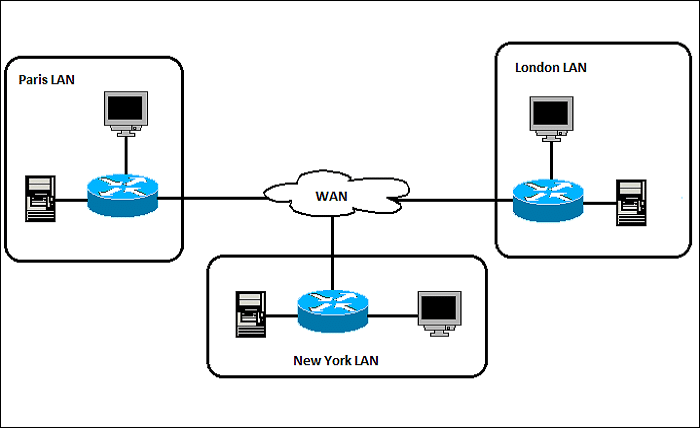
Given the accelerating pace of digital transformation, robust and all-encompassing networking solutions have become paramount. Wide Area Networks (WANs) have emerged as a critical linchpin in facilitating global communication, connecting geographically dispersed networks over vast distances. Understanding various WAN concepts allows organizations to enhance data transmission capabilities and ensure seamless interaction across local and international borders. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of WANs and their continuing significance in modern network infrastructure.
WANs play a pivotal role by bridging communication gaps between different locales, making them indispensable for businesses and institutions with global footprints. They have transformed businesses’ operations, allowing remote collaboration, improved data accessibility, and reliable global communication. The importance of WANs in network architecture is growing as technology advances, necessitating a closer examination of their advantages, difficulties, and future.
Introduction to WANs
A Wide Area Network (WAN) fundamentally differs from a Local Area Network (LAN) by its ability to connect users and devices over vast geographical distances, spanning cities, countries, and even continents. This broad reach is essential for businesses with various locations since it allows teams to collaborate and communicate efficiently, regardless of location.
WANs are meticulously designed to accommodate high-volume data exchanges and extensive communication needs, making them essential for maintaining productivity and connectivity in modern enterprises’ increasingly complex landscapes. These networks often utilize communication technologies, including leased lines, satellite links, and fiber-optic cables, to ensure reliable and high-speed data transmission.
The WAN concepts in an organization cannot be overstated; they serve as the backbone of critical business operations. By facilitating efficient connectivity solutions, WANs ensure employees can access information, applications, and resources needed to perform their duties effectively. In today’s fast-paced corporate world, this interconnection helps the organization’s overall agility and responsiveness by supporting day-to-day operations and strategic initiatives like cloud computing, remote work, and international cooperation.
WANs vs. LANs: Key Differences
While wide-area networks (WANs) and local-area networks (LANs) share the fundamental objective of facilitating connectivity among devices for unhindered communication, they vary significantly in scope, scale, and the technologies underlying their operations.
Local Area Networks (LANs) are typically confined to smaller geographical areas, such as a single building, office space, or residential home. These networks provide high-speed data transmission, often utilizing technologies such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi, to ensure rapid and efficient communication among devices within proximity. The limited range of LANs allows them to deliver low latency and high bandwidth, making them ideal for applications that require quick responses, like file sharing, gaming, or streaming media.
On the other hand, wide-area networks (WANs) cover much larger geographical areas, connecting multiple LANs that may be situated in different cities, regions, or even countries. Due to their extensive reach, WANs often employ a more complex array of technologies, including leased lines, satellite links, and MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), to manage data traffic across vast distances. This complexity is necessary to handle issues such as varying bandwidth availability, latency, and data routing through multiple intermediary devices.
The stark contrast between the two types of networks highlights the diverse technologies and management strategies integral to their operation. For instance, while managing a LAN can often be as straightforward as configuring a single router or switch, managing a WAN necessitates sophisticated network management software and protocols to ensure data integrity and optimal performance across a sprawling infrastructure. Ultimately, these differences underscore the critical role that each type of network plays in supporting various communication needs within our increasingly interconnected world.
Benefits of Using WANs
Wide Area Networks (WANs) provide many invaluable benefits critical for the operational efficiency of contemporary businesses and institutions. One of their main benefits is the ability of WANs to create seamless communication across geographically separated offices. This interconnectedness facilitates effective resource sharing, as teams can easily access shared files, applications, and databases regardless of their physical locations.
By facilitating a variety of communication modes, including VoIP, video conferencing, and instant messaging, WANs improve client and stakeholder communication and resource sharing. This leads to improved collaboration and faster decision-making processes, essential in the increasingly fast-paced business environment.
Moreover, WANs support companies in delivering a consistent network experience for remote employees, ensuring that operations run smoothly despite geographical constraints. It is vital for industries that rely on a distributed workforce, such as technology, healthcare, and global logistics, where reliable connectivity is advantageous and a fundamental requirement for maintaining productivity and achieving organizational success.
By offering these strong network features, WANs enable companies to be flexible and adaptable to the shifting market needs, strengthening their position as market leaders.
Challenges with WANs
While wide-area networks (WANs) offer numerous advantages, their deployment and management present various complex challenges that organizations must navigate. One of the primary concerns is the considerable setup costs associated with establishing a robust WAN infrastructure. These expenses include hardware procurement, software licensing, and the costs of skilled personnel required for implementation and maintenance.
Moreover, WANs are often susceptible to various security vulnerabilities. Organizations risk unauthorized access and potential data breaches, which can result in severe implications for operational integrity and customer trust. To counter these threats, organizations need to implement a multi-layered security approach. It should have intrusion detection systems (IDS) that actively detect and react to unusual network activity, sophisticated firewalls that monitor and filter incoming and outgoing traffic, and strong encryption methods to protect data in transit.
Addressing latency issues is crucial for optimal WAN performance and security measures. High latency can adversely affect applications, particularly real-time services such as video conferencing and VoIP communications. Organizations should employ network optimization techniques to reduce latency and enhance bandwidth utilization to mitigate these effects. Strategies may involve traffic shaping, caching techniques, and quality of service controls to guarantee that the network runs effectively and provides excellent performance across vast geographic regions.
By taking a holistic approach that encompasses security and performance optimization, organizations can effectively manage the complexities of WANs, ensuring they serve their intended purpose of connectivity and communication over long distances.
WAN Technologies in the Modern Era
The ongoing evolution of WAN technology continually reshapes how networks are managed and optimized. With better network performance and lower costs than traditional WAN topologies, technologies like Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) are becoming increasingly popular. Insights from Network World highlight how these advancements enable WANs to become more adaptive, streamlined, and efficient in meeting modern networking demands.
Future Trends in WAN Development
Looking to the future, trends such as the integration of 5G advancements, AI-driven network management, and greater cloud incorporation are poised to propel WAN development further. As the IEEE discusses, these innovations are set to introduce a new era of connectivity, positioning WANs at the forefront of cutting-edge technological advancements. Organizations must stay informed and ready to integrate these evolving technologies to harness the full potential of WAN infrastructure.
Conclusion: The Continuing Evolution of WANs
WANs remain foundational to effective network strategies as enterprises thrive in an increasingly interconnected and globalized environment. By embracing technological innovations and proactively addressing the challenges inherent in WAN deployment, organizations can leverage WANs to support resilient, efficient, and world-spanning networks that drive productivity and success.




